Installation & First Scan
A step-by-step guide to establishing the secure bridge between your Google Doc and the Inkable accessibility engine.
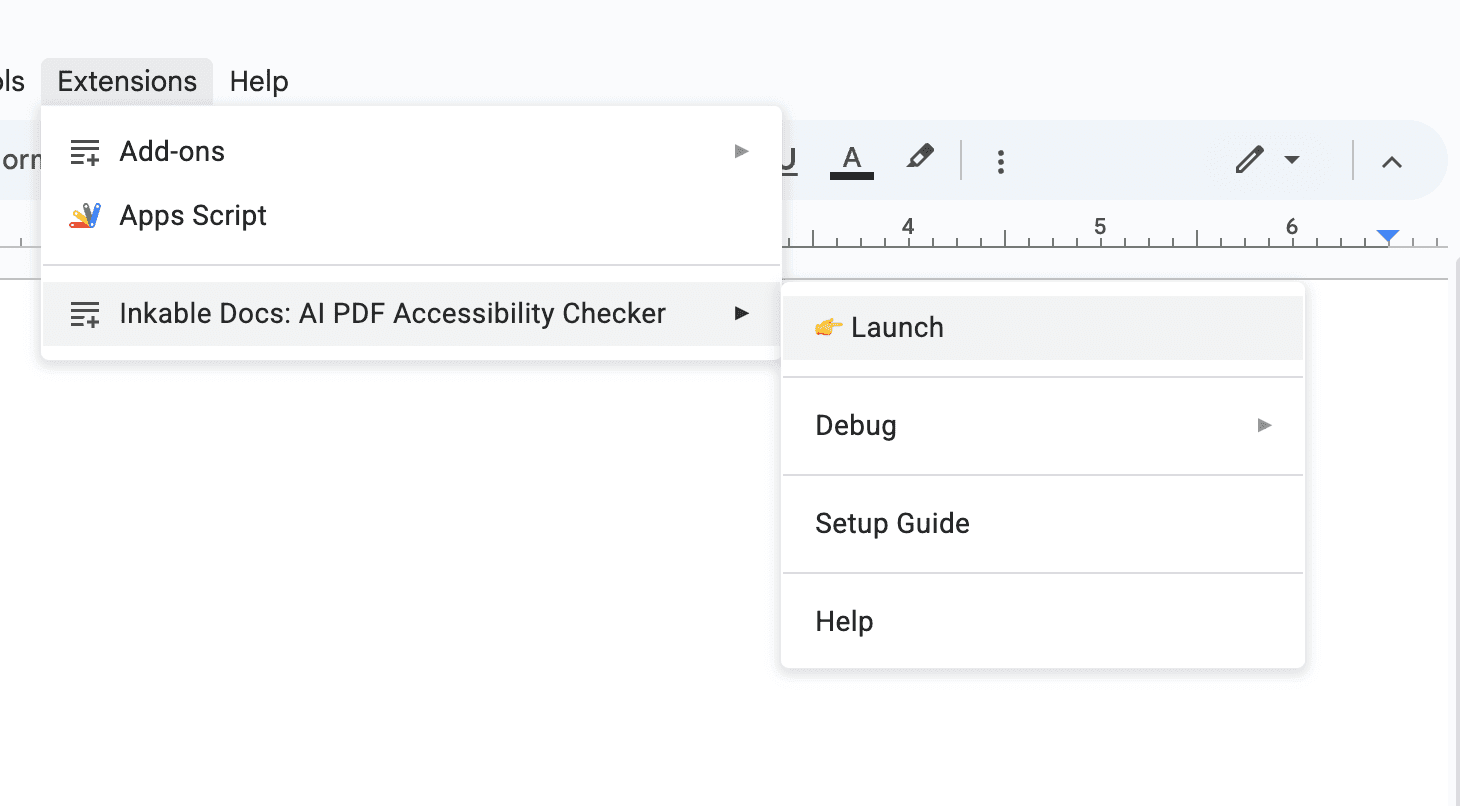
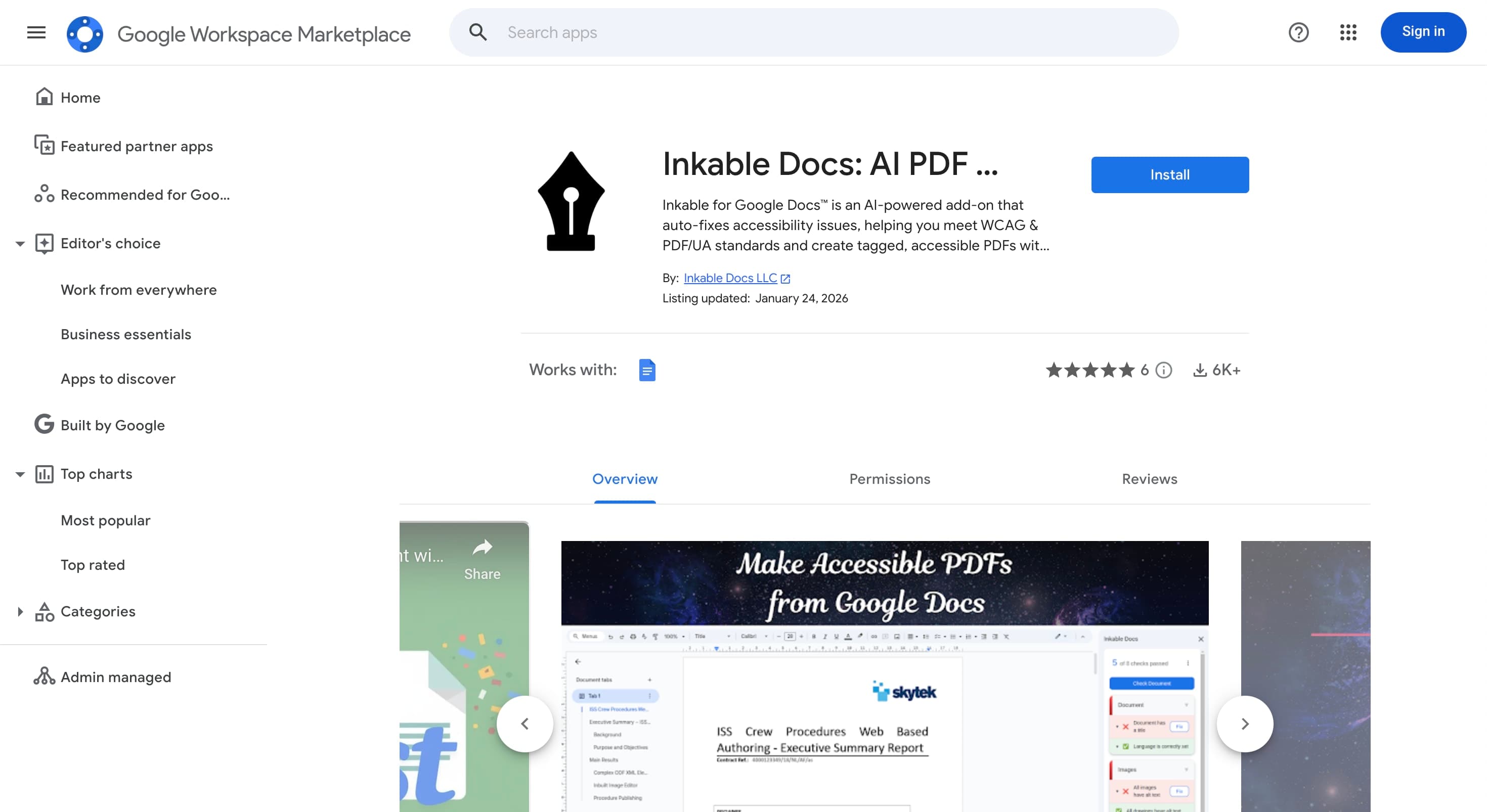
Marketplace Installation
The add-on lives in the Google Workspace Marketplace. You must grant permission for the add-on to read the active document content to perform scans.
Required Step:
- Search "Inkable Docs"
- Click Install
- Approve Google OAuth scopes
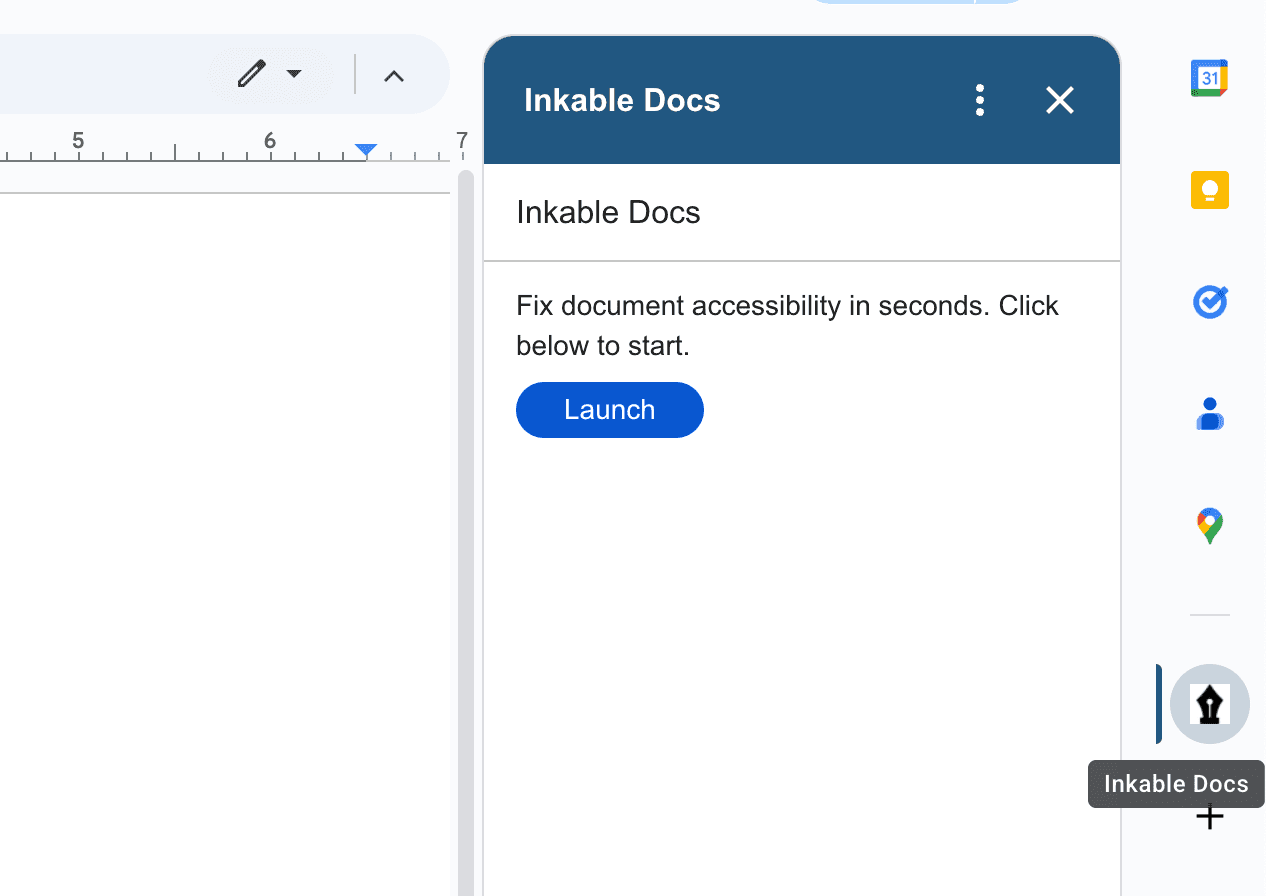
Authentication & Sync
When you launch the sidebar, Inkable automatically logs you in using your Google account. No sign-in required—just launch the sidebar and you're ready to go.
The Automatic First Scan
The sidebar automatically triggers a full Document Check on launch. This is an operational requirement to establish the current accessibility baseline.
What is scanned:
- All heading levels and hierarchical nesting
- Image alternative text and decorative state
- Table structural associations and headers
For a complete list of all 16 accessibility checks performed, see the Accessibility Checks Reference section below.

Accessibility Checks Reference
Inkable performs 16 accessibility-related checks across five categories. These checks are aligned with PDF/UA (ISO 14289-1) and WCAG 2.1 concepts to help ensure your documents meet accessibility requirements.
Check Types
Required: Most checks are required for PDF/UA conformance and must pass for full accessibility compliance.
Advisory: Some checks are best practices that improve accessibility but are not strictly required by PDF/UA standards.
Document
Document has a title
Ensures the document has a descriptive title (dc:title) with DisplayDocTitle set to true. Required for PDF/UA conformance and essential for screen readers and document navigation.
Reference: PDF/UA (ISO 14289-1), WCAG 2.4.2
Language is correctly set
Verifies that the document's natural language is properly declared in document properties. A hard PDF/UA requirement critical for screen readers to use correct pronunciation and language-specific features.
Reference: PDF/UA (ISO 14289-1), WCAG 3.1.1
Images
All images have alt text
Checks that Figure tags have Alt or ActualText attributes, unless they are marked as artifacts. PDF/UA requires all non-decorative images to have alternative text that describes their content or function.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.1.1
All drawings have alt text
Ensures drawings, shapes, and other graphical elements (also tagged as Figure in PDF/UA) have descriptive alternative text. This is a UI distinction; PDF/UA treats both images and drawings as Figure elements.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.1.1
Decorative media marked
Verifies that purely decorative images, shapes, or graphics are properly marked as artifacts so screen readers can ignore them. PDF/UA requires decorative content to be artifacts.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.1.1
Equations have descriptions
Checks that Formula tags have Alt attributes with descriptions that convey their meaning to assistive technologies. Required for PDF/UA conformance.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.1.1
Headings
Heading semantics are appropriate
Validates that headings use proper H tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) rather than styled text. Proper heading tags are required for PDF/UA conformance and enable proper document structure navigation.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.3.1
Heading order is logical
Ensures headings follow a logical hierarchy without skipping levels (e.g., H1 → H3 without H2). Skipping heading levels is explicitly disallowed in numbered heading sequences per PDF/UA.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.3.1
Tables
Column and row headers are properly tagged
Verifies that table headers are correctly identified and associated with their corresponding data cells. This is core PDF/UA table structure and essential for screen reader navigation of tabular data.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.3.1
Tables avoid merged cells
Warns about merged or spanned cells that may complicate screen reader navigation. PDF/UA does not forbid merged cells but requires headers and scope to remain unambiguous. Complex structures may need careful markup.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.3.1
Layout tables are marked
Identifies content that uses table-like formatting but does not convey tabular relationships. Such content should not be tagged as Table elements or should be marked as artifacts so assistive technologies can ignore them.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.3.1
Content Readability
Lists used for sequences
Verifies that sequential or related items are formatted as proper List elements (ordered or unordered) rather than plain text with line breaks or numbers. Lists must be tagged when content is intended as a list.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.3.1
Links are informative
Checks that hyperlinks have alternate descriptions (Contents entry) that convey their purpose. PDF/UA requires links to have alternate descriptions, and descriptive link text is recommended for clarity.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 2.4.4
TOC included
AdvisoryVerifies that documents with multiple sections include a table of contents, properly tagged for navigation. This is a best practice for long documents; PDF/UA does not require a TOC, and WCAG 2.4.5 suggests "multiple ways" rather than mandating a TOC.
Reference: Best Practice (aligned with WCAG 2.4.5 concepts)
Headers/Footers are decorative
Ensures that header and footer content (like page numbers, document titles) are marked as artifacts when they are decorative or repetitive, so assistive technologies can ignore them.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.3.1
Text colors are readable
Validates that text has sufficient color contrast and that information is not conveyed by color alone. PDF/UA references contrast requirements but does not define specific numeric ratios like WCAG 1.4.3. Ensures readability for users with visual impairments.
Reference: PDF/UA (Matterhorn Protocol), WCAG 1.4.3